RNA model: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
Furthermore, the configuration files need to be generated so that the nucleotides are positioned so that they satisfy RNA potentials (for instance in the case of duplex, they need to be initialized in an A-helical structure). For this purpose, a script <tt>generate-RNA.py</tt> is provided in <tt>UTILS/</tt> subdirectory of the source code main directory. | Furthermore, the configuration files need to be generated so that the nucleotides are positioned so that they satisfy RNA potentials (for instance in the case of duplex, they need to be initialized in an A-helical structure). For this purpose, a script <tt>generate-RNA.py</tt> is provided in <tt>UTILS/</tt> subdirectory of the source code main directory. | ||
For instance, if one wants to generate an initial configuration of three strands, two of them complementary (with sequence 3'-GCAAGUCG-5' and its complementary) and in a duplex configuration, and one single strand with sequence 3'-ACCCGU-5', one needs to create the following file text file, called for example <tt> | For instance, if one wants to generate an initial configuration of three strands, two of them complementary (with sequence 3'-GCAAGUCG-5' and its complementary) and in a duplex configuration, and one single strand with sequence 3'-ACCCGU-5', one needs to create the following file text file, called for example <tt>sequences.txt</tt>: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
DOUBLE GCAAGUCG | DOUBLE GCAAGUCG | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
In order to create the initial configuration files <tt>generated.top</tt> and <tt>generated.conf</tt> with the duplex and single strand randomly placed in a simulation cube with side of length 20 in simulation units, run the script | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
./generate-RNA.py | ./generate-RNA.py sequences.txt generated 20.0 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
. | which will created the configuration files. Those can then be used as initial configuration for the simulations. Other input command options that apply to oxDNA, such as use of external forces, apply with the same syntax to oxRNA as well and are described in more detail in the model documentation. | ||
For an example on how to use VMMC simulations to determine the melting temperature of an RNA duplex, please see the following tutorial: [[RNA_duplex_melting]] | |||
===Visualization of RNA configurations=== | |||
In order to visualize the configurations of oxRNA model, one can use the <tt>traj2chimera.py</tt> script, as described for the oxDNA model. It is however necessary to first set environment variable <tt>OXRNA</tt> to 1 in order for the script to properly generate visual representation of oxRNA: | |||
<pre> | |||
export OXRNA=1 | |||
</pre> | |||
The visualization of configuration specified in, for example, <tt>generated.top</tt> and <tt>generated.conf</tt> can be then obtained by running | |||
<pre> | |||
traj2chimera.py generated.conf generated.top | |||
</pre> | |||
in the <tt>UTILS/</tt> directory | |||
which creates files <tt>generated.conf.pdb</tt> and <tt>chimera.com</tt> which can then be visualized with [http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/download.html Chimera software] | |||
by running the following command: | |||
<pre> | |||
chimera generated.conf.pdb chimera.com | |||
</pre> | |||
or alternatively, you can load <tt>generated.conf.pdb</tt> in the Chimera software and then click on Tools->General Controls->Command line and specify | |||
<pre> | |||
read chimera.com | |||
</pre> | |||
in the command line, where <tt>chimera.com</tt> needs to be present in the directory where you started Chimera. | |||
===References==== | |||
The model and its performance is discussed in detail in the following reference: | The model and its performance is discussed in detail in the following reference: | ||
P. Šulc, F. Romano, T. E. Ouldridge, J. P. K. Doye, A. A. Louis: A nucleotide-level coarse-grained model of RNA, submitted | P. Šulc, F. Romano, T. E. Ouldridge, J. P. K. Doye, A. A. Louis: A nucleotide-level coarse-grained model of RNA, submitted | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 10 March 2014
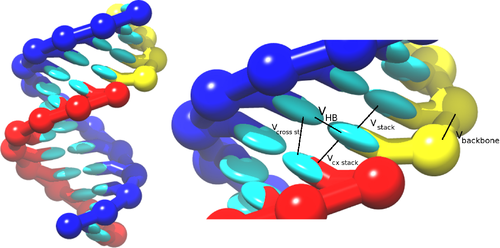
The RNA model, oxRNA, treats each RNA nucleotide as a single rigid body with multiple interaction sites, following the coarse-graining apporach adopted for the DNA model. The nucleotides interact with pairwise interaction potentials, which are listed below:
- Backbone connectivity ,
- Excluded volume ,
- Hydrogen bonding ,
- Nearest-neighbour stacking ,
- Cross-stacking between base-pair steps in a duplex ,
- Coaxial stacking .
which are schematically illustrated in the picture:
Simulation units
The code uses dimensionless energy, mass, length and timescales for convenience. The relationship between simulation units (SU) and SI units is given below.
| Simulation unit | Physical unit |
|---|---|
| 1 unit of length | 8.518x10 m |
| 1 unit of energy | 4.142x10 J |
| 1 unit of temperature | 3000 K |
| 1 unit of force | 4.863x10 N |
| 1 unit of mass | 5.34x10 kg |
| 1 unit of time | 3.06x10 s |
Running simulation with the oxRNA model
The oxRNA model is integrated into the oxDNA simulation code. In particular, it is possible to use Virtual Move Monte Carlo (VMMC), Monte Carlo (MC) and Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulation algorithms using the same format of input file as for the DNA model, with the following additional line included in the input file to specify RNA model:
interaction_type = RNA
The RNA model comes with two parametrizations, the average-base and sequence-dependent one. In the average-base parametrization, the interaction strengths are the same for all Watson-Crick and wobble base pairs (AU, GC, GU) and 0 for all other types of base pairs. The interaction strengths have the same strength for all possible pairs of nucleotides interacting with stacking interaction . In the sequence-dependent version of the model, the interaction strengths of and depend on the type of interacting bases.
The average-base parametrization is used by default. In order to use the sequence-dependent version of the model, the following options need to be added into the input file:
use_average_seq = 0 seq_dep_file = rna_sequence_dependent_parameters.txt
Note that the file rna_sequence_dependent_parameters.txt needs to be located in the directory where you run the simulation, or full location of the file needs to be specified in seq_dep_file option.
Furthermore, the configuration files need to be generated so that the nucleotides are positioned so that they satisfy RNA potentials (for instance in the case of duplex, they need to be initialized in an A-helical structure). For this purpose, a script generate-RNA.py is provided in UTILS/ subdirectory of the source code main directory. For instance, if one wants to generate an initial configuration of three strands, two of them complementary (with sequence 3'-GCAAGUCG-5' and its complementary) and in a duplex configuration, and one single strand with sequence 3'-ACCCGU-5', one needs to create the following file text file, called for example sequences.txt:
DOUBLE GCAAGUCG ACCCGU
In order to create the initial configuration files generated.top and generated.conf with the duplex and single strand randomly placed in a simulation cube with side of length 20 in simulation units, run the script
./generate-RNA.py sequences.txt generated 20.0
which will created the configuration files. Those can then be used as initial configuration for the simulations. Other input command options that apply to oxDNA, such as use of external forces, apply with the same syntax to oxRNA as well and are described in more detail in the model documentation.
For an example on how to use VMMC simulations to determine the melting temperature of an RNA duplex, please see the following tutorial: RNA_duplex_melting
Visualization of RNA configurations
In order to visualize the configurations of oxRNA model, one can use the traj2chimera.py script, as described for the oxDNA model. It is however necessary to first set environment variable OXRNA to 1 in order for the script to properly generate visual representation of oxRNA:
export OXRNA=1
The visualization of configuration specified in, for example, generated.top and generated.conf can be then obtained by running
traj2chimera.py generated.conf generated.top
in the UTILS/ directory which creates files generated.conf.pdb and chimera.com which can then be visualized with Chimera software by running the following command:
chimera generated.conf.pdb chimera.com
or alternatively, you can load generated.conf.pdb in the Chimera software and then click on Tools->General Controls->Command line and specify
read chimera.com
in the command line, where chimera.com needs to be present in the directory where you started Chimera.
References=
The model and its performance is discussed in detail in the following reference:
P. Šulc, F. Romano, T. E. Ouldridge, J. P. K. Doye, A. A. Louis: A nucleotide-level coarse-grained model of RNA, submitted